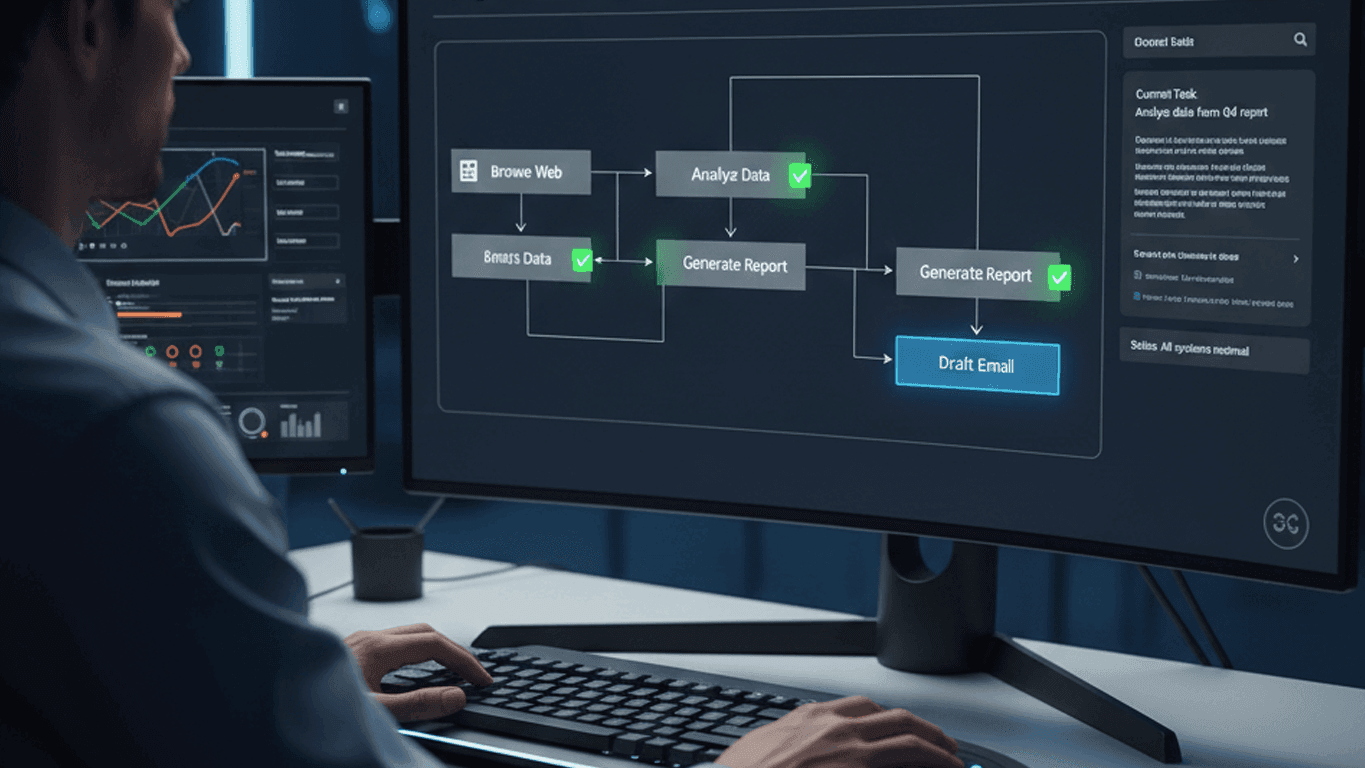
While chatbots respond to individual prompts, AI agents can plan multi-step workflows, use tools, and execute tasks autonomously. This shift from reactive AI to agentic AI represents the next major evolution in software automation.
What Are AI Agents?
An AI agent is a system that can:
- Perceive its environment through inputs and data
- Reason about what actions to take
- Plan multi-step sequences to achieve goals
- Act by executing tools, APIs, and workflows
- Learn from outcomes to improve future performance
Unlike a chatbot that answers one question at a time, an agent can be given a high-level goal and autonomously determine the steps needed to achieve it.
Real-World Applications
Customer Service Automation
AI agents can handle complex customer inquiries that span multiple systems — checking order status, processing returns, updating accounts, and escalating to humans only when necessary.
Software Development
Coding agents can read requirements, write code, run tests, fix bugs, and submit pull requests. While not replacing developers, they handle routine tasks with increasing reliability.
Data Analysis
Agents can be given a business question, determine which data sources to query, write and execute analysis code, generate visualizations, and summarize findings.
DevOps Automation
AI agents can monitor systems, diagnose issues, execute remediation steps, and learn from incidents to prevent future occurrences.
Building Effective Agents
Tool Integration
Agents are only as capable as the tools available to them. Integrating APIs, databases, file systems, and external services expands what agents can accomplish.
Guardrails
Autonomous systems need boundaries. Define what actions agents can take independently and what requires human approval. Implement rate limits, budget constraints, and safety checks.
Observability
Understanding what an agent is doing and why is critical. Comprehensive logging of the agent's reasoning, tool calls, and decisions enables debugging and improvement.
Human-in-the-Loop
The most effective agent systems include checkpoints where humans review and approve critical actions. Full autonomy should be earned through demonstrated reliability.
Challenges and Limitations
- Reliability — Agents can make compounding errors across multi-step workflows
- Cost — Complex agent tasks may require many LLM calls, increasing costs
- Evaluation — Measuring agent performance on open-ended tasks is difficult
- Security — Autonomous agents with tool access present new security considerations
The Path Forward
AI agents are evolving rapidly. The organizations that invest in understanding and integrating agentic AI today will have a significant advantage as the technology matures. Start with well-defined, low-risk workflows and expand as you build confidence and expertise.